What is IPC in Processors? – Technopath
Processor manufacturers such as AMD and Intel mention some performance and efficiency figures with the CPU series they introduce every year. When it comes to performance, one of the terms we sometimes encounter is IPC (instructions per cycle/clock). Is it important? Yes it is important. Sometimes gains of up to 15-20% compared to the previous generation are mentioned.
This is something foreign to many tech enthusiasts and the explanation is a bit complicated. IPC refers to the number of instructions a CPU can process in a single clock cycle. We know the short description is not enough, now we will go into more detail.
What is IPC?
Clock speed tells you how many cycles a CPU can complete in one second, while IPC (instructions per cycle/clock) tells you how many power points a CPU can complete per cycle. rev defines what it can perform.
For example, a processor with a faster clock speed can complete more cycles per second, while a processor with a higher IPC but lower clock speed can still complete more cycles per second. ¶can complete the rev. As a result, when talking about a faster CPU, it is more accurate to mention both clock speed, IPC and core numbers.
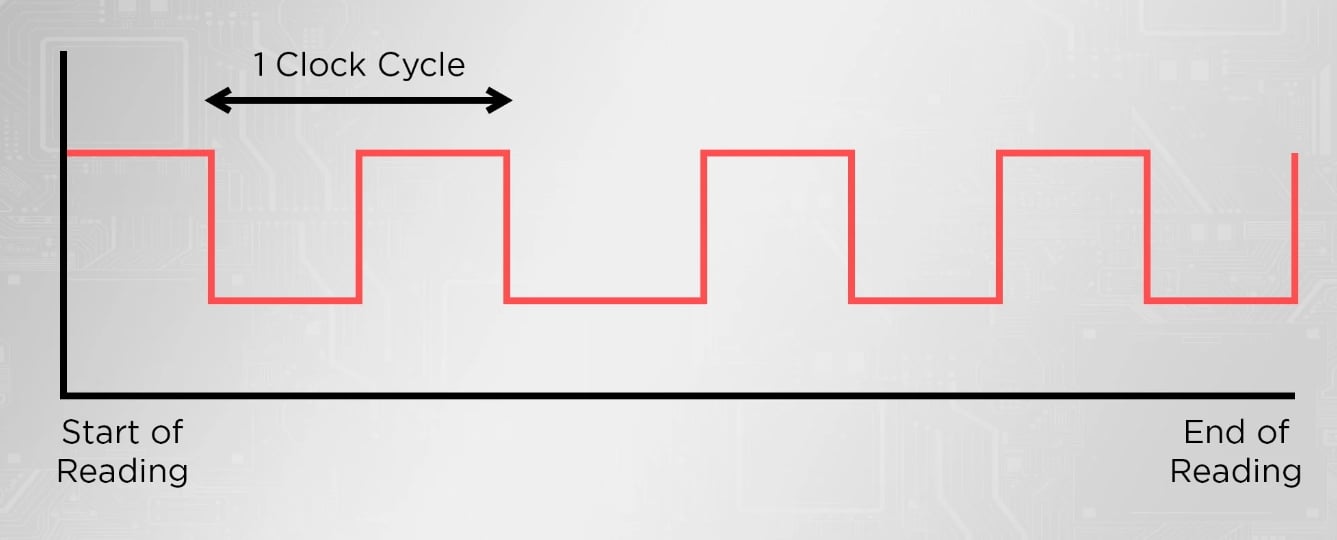
Digital circuits rely on clock signals to know when and how to execute instructions. That’s why most electronic devices, including CPUs, have an internal oscillator (clock) to maintain a constant clock cycle. These clock signals are continuous and appear as a simple square wave with a high/low state.
A ‘loop’ in the CPU is the time interval between two of these pulses synchronized by this internal oscillator. So, 1 is the time it takes to go from a low state to a high state and back to a low state again.
A loop in the processor indicates the time interval between two of the pulses synchronized by the internal oscillator. In other words, we can define it as the time it takes to go from a low state to a high state and back to a low state again. The number of these ‘cycles’ it can process per second is what we call a processor’s ‘clock speed’.
Since CPU clock cycle and clock speed can be different for each CPU architecture, never compare CPUs of different brands/generations using clock speeds alone. z. We already express this at every opportunity.
Now that you know what a clock cycle is, defining IPC becomes much easier. IPC (instructions per clock) is the number of instructions a CPU can execute in a single clock cycle. On the other hand, the clock speed of the processor (in GHz) is the number of clock cycles it can complete in one second. So, a 3 GHz CPU can complete 3 billion cycles per second.
By the way, let’s add that the IPC of any processor may vary depending on the workload. Additionally, CPU manufacturers generally do not share IPC information on their spec sheets.
For example, let’s say we have different processors and we locked them all to 3 GHz. In the meantime, architectural differences as well as the number of instructions that CPUs can process per clock cycle come into play.
 Above we see a chart showing AMD’s IPC development over the years. The Reds announced that they achieved IPC gains above the industry standard between 2017 and 2020 .
Above we see a chart showing AMD’s IPC development over the years. The Reds announced that they achieved IPC gains above the industry standard between 2017 and 2020 .
How Do They Make IPC Earnings?
CPU manufacturers are improving IPC to a greater or lesser extent with almost every new generation. Many factors may come together for this development, but let’s summarize briefly and look at another AMD introduction.
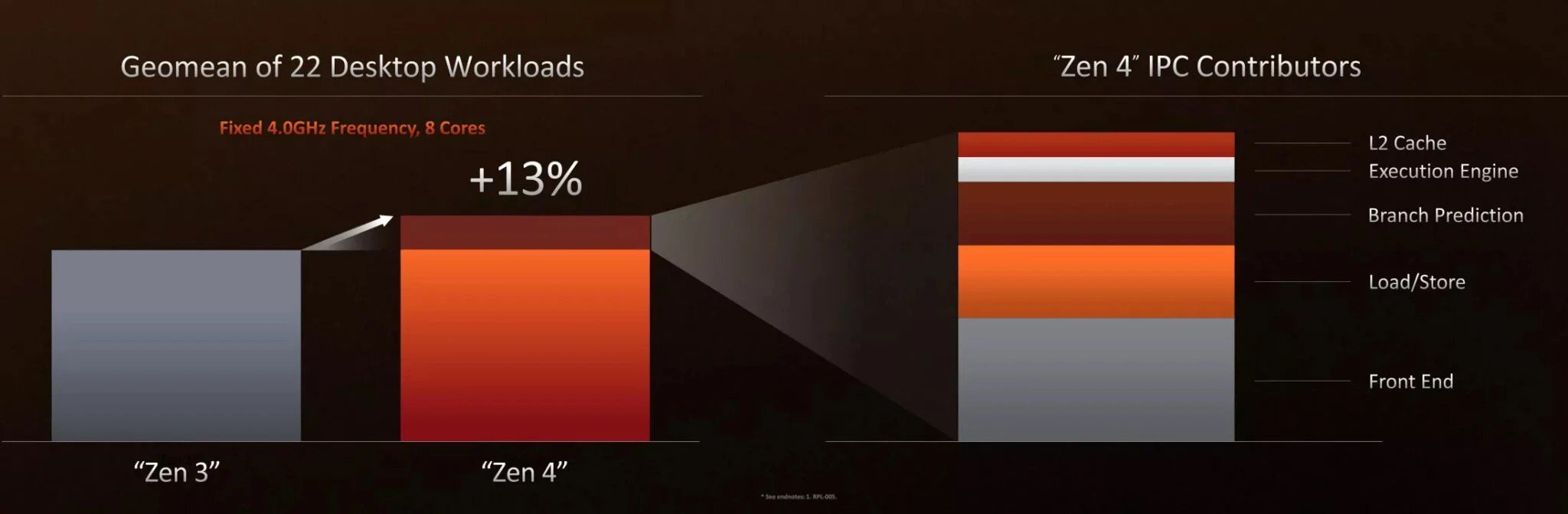
The IP designer showed that the Zen 4 architecture achieved a 13% IPC increase compared to the previous architecture. The factors listed on the right have all contributed to this IPC increase:
- L2 cache: CPUs have different types of memory, including L1, L2 and L3. Their duty is to quickly provide the most needed data to the processing unit.
- Execution Engine: Unit that performs integer and memory operations and floating point operations.
- Branch Prediction: Speeds up the processing of branch instructions by using pipelines.
- Load/Store: A special unit responsible for carrying out all loading and storage instructions.
- Front End: The part that deals with operations such as command fetching and decoding.
IPC and Clock Speed Relationship
No comparison can be made by comparing the clock speed between two different processor brands and generations. However, you can compare processors from the same generation and architecture.
It is a little difficult to explain this relationship, but let’s give an example. Let’s say two separate people will fill two separate pits with sand and they work at a constant speed of 1 shovel/second. Think of the IPC as a shovel and the clock speed as the speed at which someone is shoveling sand. If two people use the same shovel, they will finish their task at the exact same time.
But if you replace a shovel with a larger shovel and both people continue to throw sand at the same speed, the one with the larger shovel will finish the job faster. The relationship between IPC and clock speeds on the CPU is also similar.

