What is IHS in Processors? What Does the Integrated Heat Spreader Do?

Chips that go through many processes before reaching their final form can contain millions and sometimes billions of transistors. We all know how difficult semiconductor design goes through. When we look at hardware such as CPU or GPU from the outside, we actually see a monolithic design in a single piece. However, what we see is actually just an integrated heat spreader, that is, IHS (integrated heat spreader). So what is this thing called IHS?

Besides the CPU and GPU, almost all of the chips used in the devices we use are covered with an integrated heat dissipator. This small piece of metal may seem like a very simple thing, but for the chips, life is important. It not only spreads the resulting heat around, but also protects the chip and ensures its integrity.
What is IHS in Processors?
IHS, which means integrated heat dissipator, is simply the metal outer cover of the processor. It acts as both a protective shell around the processor silicon and an intermediary that allows heat exchange between the CPU and your CPU cooler.
The first processors developed did not ship with integrated heat emitters and ran unbearably hot. Mounting a heatsink directly on the CPU was a big risk because it could become trashy if too much pressure was applied. When the pressure was too light, the silicon chips turned into a ball of fire. A solution was needed for this, and then metal heat emitters came into play.

As you know, the processor core itself is quite small compared to the processor itself. On the other hand, the number of transistors used in new generation processors is quite high. As production technologies improved and transistors became smaller, the design of chips began to become more complex. A large number of cores as well as components are intertwined, thus allowing the heat generated to be concentrated in a very small area. He cried.
In summary, IHSs simply changed the game. Heat distributors, which distribute the heat produced by the CPU evenly across its surface, seem simple but are very successful in terms of functionality. ı. The heat is distributed rather than concentrated in a single point. Meanwhile, depending on the company, different thermal materials can be applied between the chip and IHS. As you know, we apply thermal paste to the outside facing surface. Thermal paste transmits the heat received from the IHS to the cooler we installed on the upper part. The heat produced is eventually discharged. Let’s briefly look at the benefits of integrated heat distributors:
- Even heat distribution: IHS prevents the chips from heating up completely by distributing the heat evenly. In this way, no part inside the processor reaches unusable temperatures.
- Protection: It’s like a helmet for your body, so to speak. It has a hard structure that protects the sensitive silicone from accidental impacts.
- Better Cooling: With an IHS, your cooling solution can do its job more effectively, like a thermostat in a well-insulated home.
- Adds Aesthetics to the Rope: Frankly, the processors look better aesthetically with integrated heat spreaders.
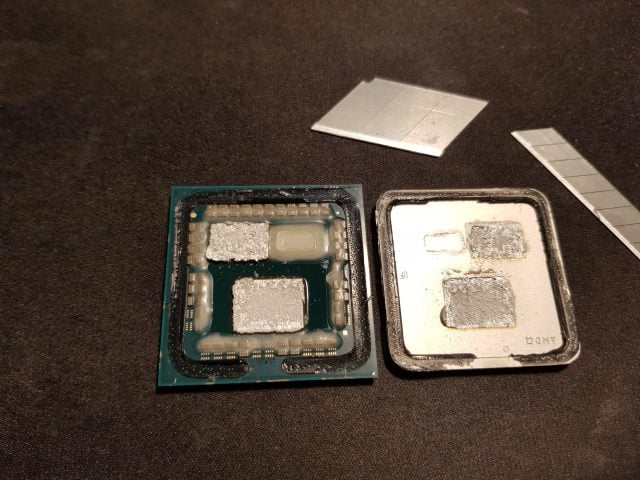
Some overclockers do a process called “delid” to remove the stock IHS of their processors and replace it with an even more conductive material. This process is actually a bit difficult and risky. However, no matter how good the IHS is, a cooler must always be used.
Delid and Liquid Metal Usage
We have seen some examples of the use of liquid metal in the past. Famous overclocker Novel ‘der8auerâ†Hartung, performed delid with Intel’s Core i9-14900K processor and applied liquid metal thermal paste to maximize thermal conductivity. Experiments have shown that the difference between the 13th Generation and 14th Generation Core CPUs is negligible, and as usual, the delid process provides a significant temperature drop. ni blood ±cracked.
Delid process was carried out with Delid-Die-Mate produced by Thermal Grizzly. However, Conductonaut Extreme liquid metal thermal paste was applied as liquid metal. A CPU contact frame was used to ensure the best possible contact with Corsair’s 360 mm all-in-one liquid cooling system.
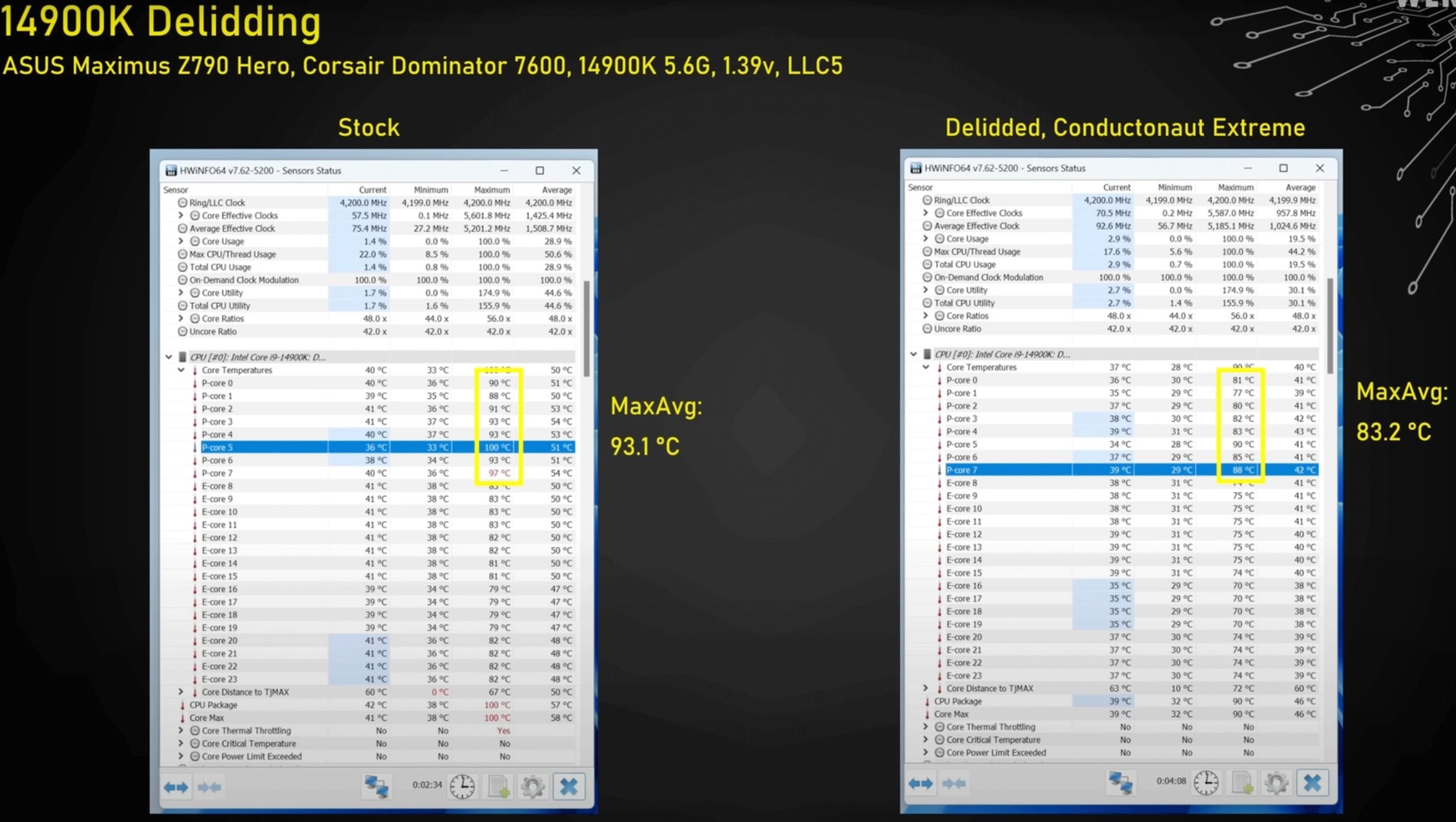
Let’s come to the temperature values. The Core i9-14900K ran 10°C cooler based on average peak temperatures, along with a slight reduction in power consumption. The temperatures of the efficiency cores, which we call E-Core, dropped by 8°C. Meanwhile, with the removal of IHS and the implementation of a better thermal interface, a 12°C decrease in the temperature of the P-Core performance cores was observed.
As you know, both the delid process and the use of liquid metal are risky. Additionally, the warranty becomes void. We hope that CPU manufacturers will use more advanced heat spreaders and materials in the future so that they will never be needed.
AMD Ryzen 7000 IHS Design
If you remember the IHS design adopted in Ryzen 7000 processors, it was very different. Technology enthusiasts were wondering about the performance of the new design, and then it turned out that the new design could not provide very good cooling performance. IHS, which resembles spider legs, has also created problems for users who want to remove thermal paste when replacing CPU coolers.

There is also the issue of thickness. The internal heat dissipator of Ryzen 7000 is thicker than previous models. The 7000 series chips are inherently thinner, but AMD’s marketing team chose to thicken the IHS to make the new AM5 CPUs compatible with older AM4 coolers.
The red team’s Ryzen 7000 processors can get very hot in some scenarios. Although it is very powerful in terms of performance, temperatures can reach very high levels. JayzTwoCentsYouTuber named  thinned the heat spreader of the Ryzen 9 7950X by 0.8 mm and reduced the temperature of the processor depending on the thermal paste used (all core in the clearing When operating at 5.10 GHz) it dropped by approximately 10 degrees Celsius. As the temperatures dropped, the frequency of the cores reached up to 5.40 GHz.
As you can see in the video, a sanding machine was used to wear down the processor IHS. The results look very good, but this process naturally voids the warranty.
AMD used a very thick (3.6 mm) heat sink in its latest Ryzen 7000 series processors to make it compatible with the AM4 form factor. Compatibility is of course a positive development for the end consumer, but when the IHS is thicker, thermal conductivity decreases and it becomes a little more difficult to cool the CPU. This means higher temperatures, lower frequency speeds and lower overclocking potential. If you remember, in our AMD Ryzen 9 7950X review, we stated that the temperatures reached 95 degrees many times.

Removing the integrated heat distributor reduces temperatures by up to 20 degrees Celsius. When the 0.8 mm etching process was performed, it was revealed that the temperature dropped between 7 and 10 degrees. Of course, such practices are risky. The integrated heat spreaders (IHS) you see on processors are used to protect sensitive CPU chips, transfer heat, and ensure proper contact with the cooling system. in is used.
The importance of Thermal Paste
As we mentioned, the thermal paste we applied on the IHS is very important in terms of heat management.
Frequently Asked Questions About Thermal Pastes
- Is it appropriate to run the processor or graphics card without thermal paste?
- No, it is not safe to use a system without thermal paste. Thermal paste provides stable cooling from the heatsink to the surface area of the processor. When not in use, the computer may overheat and crashes may occur even at startup.
- What is the correct amount of thermal paste to use?
- The amount of thermal paste should be adjusted according to the surface area of your CPU. In general, you can leave a reasonably sized dot or a single thick line in the middle of the CPU. Large CPUs need at least twice as much thermal paste as normal-sized CPUs. AMD Threadripper or Intel Xeon processors require almost a gram of thermal compound on their surface area for proper cooling.
- Is high-quality thermal paste worth buying?
- Yes, a higher quality thermal paste is generally more reliable. It is less likely to dry out, separate, or change consistency after continued use. For example, if we talk about the new Arctic MX-6, the manufacturer states that it lasts up to five years without drying out. An affordable thermal paste can also last a long time, but nothing is guaranteed.
- What is the best thermal paste for GPU?
- Thermal pastes generally used for CPUs can also be used for GPUs. However, it is important to do research before using a particular product. Compatibility varies from product to product and some high-end options are not compatible with the graphics processor. As a matter of fact, it would be beneficial to do a little research before driving.
- How often to change thermal paste?
- As a general rule, thermal paste should be replaced every year. We mentioned that some products have longer durability periods, but this is not the only point. The operating temperatures of the system are very important in drying the thermal paste. If your component does not operate hot, the replacement period may take a little longer.
- Does thermal paste have a waiting life?
- Thermal paste may dry out and exceed its ‘expiration date’. This means that the product becomes useless. Make sure to keep your thermal paste in its original packaging and completely isolate it from the external environment with the cap provided. A thermal compound stored for more than 5 years may still be usable as long as the compound does not dry out.
- Is liquid metal better than thermal paste?
- Liquid metal is actually superior to all thermal pastes because the composition allows for better and more efficient heat transfer. Liquid metal is another thermal material (TIM), just like thermal paste. It is necessary to be careful when using it, so it is useful to research issues such as the structure, usage and conductivity of liquid metals.
How to Apply Thermal Paste?
- Be sure to read the user manuals before you start. This even includes the documentation that comes with the processor cooler along with the thermal paste. Thermal pastes and CPU coolers have different details. If you have information beforehand, your chances of experiencing problems will be lower.
- If there is already thermal paste in your cooler, there is no need to use thermal paste, but you can delete this ready-applied paste if you wish.
- Every CPU and GPU has an integrated heat spreader (IHS). Squeeze a small amount of thermal paste (roughly the size of a grain of rice or a pea) into the center of the surface area.
- Now install the CPU cooler. Use gentle, top-down pressure to seat your cooler’s base plate or water block onto the CPU, and use this pressure as you attach the cooler to the mounting mechanism. ± protect. You should use enough force to prevent the cooler from slipping and distribute the thermal paste evenly, but not so hard that you bend the motherboard or damage the CPU. chiller Hold it steady as you insert it diagonally into the motherboard, securing the screws (assuming you’re using a screw mechanism) as if you were drawing an ‘X’ with them. Do not fully tighten the screws until you have installed all four, then turn each one a few times before moving on to the next to ensure even pressure.
- If you wish, you can spread the thermal paste evenly on the IHS using the supplied tools or a material at home before installing the processor cooler.
- Everything is ok. But then make sure that the cooler is seated properly and working properly. Also make sure that there is no thermal paste residue leaking from the sides of the processor or anywhere on the motherboard. If you apply too much thermal paste, it may overflow from the edges. If such a situation occurs, you will need to clean it with some materials such as alcohol.
- Finally, monitor temperatures several times while using the system.

