Zen 5, RDNA 3.5 and XDNA 2: Ryzen AI 300 Mobile Processors Introduced

Taking the stage at the Computex 2024 fair held in Taipei, Taiwan, AMD introduced its new Ryzen AI 300 processors, codenamed ‘Strix Point’. The chips that will provide processing power to consumers on the mobile platform were designed with two different types of cores. These processors are powered by the Zen 5 architecture, the improved RDNA 3.5 graphics architecture and the XDNA 2 NPU unit, which enables running artificial intelligence workloads locally.
In AMD’s new branding scheme, the word ‘AI’ is now carried directly into the name of the chip. The familiar Ryzen branding has been retained, but AMD now directly identifies its NPU-equipped chips with the “AI†moniker. And perhaps most importantly, the numbering system has been reset. AMD is now here with a new series starting from Ryzen Mobile 300 instead of the 9000 series.
The AI-focused XDNA 2 neural processing unit can deliver 50 TOPS performance, which is a 5-fold gain for the third generation of AI chips. Its performance level of 50 TOPS surpasses all other chips for Windows PCs, including Qualcomm’s promising Snapdragon X Elite. In other words, it allows Copilot elements to run natively, easily exceeding Microsoft’s 40 TOPS requirement for next-generation AI computers.
AMD Ryzen AI 300 Series Features
Although AI chips have a fairly wide TDP range of 15-54W, they can be used in a wide range of devices, from ultrabooks to desktop replacement laptops. Ryzen AI 300 series is launching with two new models, and these chips come as a single monolithic die. The flagship Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 has 12 cores and 24 threads running at 2.0 GHz base and 5.1 GHz peak speed. But as you can see in the block diagram, the chip carries 4 standard Zen 5 cores and 8 optimized Zen 5c cores on a single monolithic die along with the GPU and NPU cores.
With this development, smaller Zen 4c cores were used for the first time in the top-level Ryzen 9 mobile family. Because these cores were previously limited to Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 3 Hawk Point models. Zen 5c cores are designed to take up less space on the processor die compared to ‘standard’ Zen 5 performance cores and offer sufficient performance for lighter tasks; Thus, power savings are achieved, and at the same time, chip space can be used more efficiently.
Zen 5c is actually technically similar to Intel’s cores called E-Core, but there are some differences. Zen 5c uses the same microarchitecture as the standard Zen 5 cores, with the smaller cores supporting all features intact. On the other hand, Intel’s design has different architectures and feature support. The smaller Zen 5c cores run at lower clock speeds and therefore have less peak performance than standard cores.
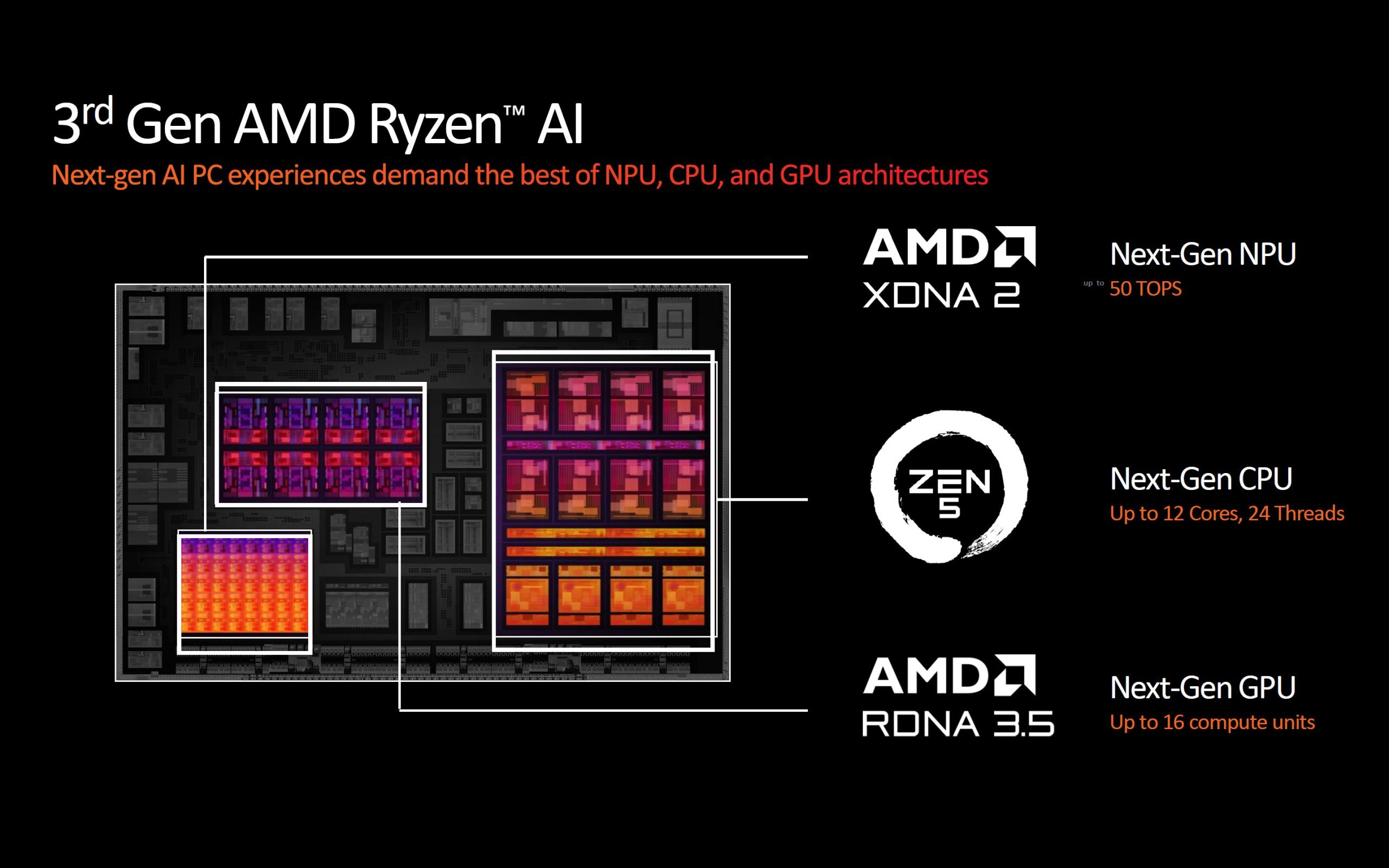
Both Zen 5 and Zen 5c cores come with threading. AMD has not yet shared the detailed specifications of the smaller cores, but assume that the boost clock is only valid for the four standard cores. We are doing it. The Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 model features the new RDNA 3.5 Radeon 890M graphics engine with 36 MB total L3 cache, 50 TOPS XDNA 2 NPU and 16 CUs running at 2.9 GHz ±yor. Although the TDP value is determined as 28W, a wide cTDP range of 15-54W is given. In other words, power adjustments can be made depending on the manufacturer.
Ryzen AI 9 365 is distributed between 4 standard Zen 5 cores and 6 density-optimized Zen 5c cores, with a base speed of 2.0 GHz and a peak speed of 5.0 GHz ±na It has a total of 10 cores. The chip also includes a 50 TOPS NPU and a 12-CU RDNA 3.5 Radeon 880M graphics engine running at 2.9 GHz. Despite the lower CPU and GPU core counts, this chip is listed with a 28W TDP like its bigger sibling.
AMD’s previous generation 7040 and 8040 series consisted of nine models. While the Ryzen AI 300 series includes only 2 models, it stands out as the first series focused on “artificial intelligence”.
| nuclei | Base Frequency | Turbo Frequency |
L3 cache |
Integrated GPU | NPU | TDP | |
| Ryzen AI 9HX 370 | 4x Zen 5 8x Zen5c (24 Threads) |
2.0GHz | 5.1GHz | 24MB | Radeon 890M 16 CU |
XDNA 2 (50 TOPS) |
15-54W |
| Ryzen AI 9 365 | 4x Zen 5 6x Zen5c (20 Work Particles) |
2.0GHz | 5.0GHz | 24MB | Radeon 880M 12 CU |
XDNA 2 (50 TOPS) |
15-54W |
Zen 5, Zen 5c and RDNA 3.5 in One
AMD announced that the new Zen 5 microarchitecture provides a 16% IPC increase compared to Zen 4. New chips produced with new process technology (TSMC 4nm) will provide great gains in both performance and power efficiency at a certain power level, especially with the addition of Zen 5c cores.
Previously, integrated graphics had a maximum of 12 CUs, that is, computing units. With the new RDNA 3.5 architecture, the number of CUs increased significantly to 16. By the way, let us note that Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 has 16 computing units and Ryzen AI 9 365 has 12 computing units. The company did not share detailed information about the changes related to the new graphics architecture. We will continue to update the information as time goes by.
New Nomenclature in AI Mobile Chips
AMD’s model numbering reset begins with the 300 series. Strix Point is named this way because it is the third series of AMD’s mobile artificial intelligence chips with NPU. The 7040 ‘Phoenix’ and 8040 ‘Hawk Point’ chips represented the first two generations, respectively. Strix Point came with a completely new name.
AMD’s previous generation chips were divided into groups defined by TDP, such as the U-, HS- and H-series (15/28W, 35W, 45W TDPs respectively). In the new series, there is no statement about the TDP level. Any Strix Point chip can be classified by the OEM in the 15W to 54W cTDP (configurable TDP) group, just like previous generation models.
The Ryzen AI 300 naming system is quite easy to define. The name Ryzen AI indicates that there is an integrated NPU within the silicon. The 9/HX part of the nomenclature indicates the product class. The last part, 370, is more interesting. The number 3 indicates the series, according to AMD’s branding, it has a third-generation NPU, while the last two digits indicate the part number and SKU.
If you remember, Intel also reset its own mobile product naming system and launched the Core Ultra 100 series. On the other hand, Intel is preparing to introduce the Core Ultra 200 series, codenamed Lunar Lake, soon. AMD has made the mobile processor numbering system similar to its rival, but with a higher numbering of 300 instead of 100.

With TDP no longer a brand measurement bar, the new descriptors only refer to a ‘brand level’. For example, the Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 moniker indicates that the chip is a Ryzen 9 model in the HX category. The name HX proves that this is a high-performance high-end model.
AMD XDNA 2 NPU Architecture
Many details have been shared about the new XDNA 2 neural processing unit (NPU), which focuses on artificial intelligence processes. AMD is the first x86 chip to bring NPUs to both mobile and desktop markets. was the manufacturer and the first generation Phoenix chips offered 10 TOPS performance. This was later increased to 16 TOPS with the Hawk Point refresh, mostly due to increased NPU clock speeds.
The Strix Point family takes AI performance to a whole new level. The redesigned XDNA 2 engine delivers up to 50 TOPS of performance at both INT8 (which is how most NPU benchmarks are determined) and FP16.

Looking at the block diagram of the new XDNA 2 engine, there are 3.5 times more “AI units”, previously called AIE-ML. Apparently DM units ( combined with the new AI unit (used for scalar calculations). The new engine appears to be much more complex and therefore more performant, but no further details are available.
NPUs are typically characterized by performance on INT8 workloads, which is a less precise data type that uses less computation and memory to run a model. However, the models must be quantized to INT8 format and lose some precision in the process. AMD’s XDNA 2 architecture is the first x86 NPU to support Block BF16, a new data format that provides the full fidelity of FP16 with many of the same processing and memory features of INT8. AMD states that Block FP16 has a plug-and-play feature; It says it doesn’t require quantization, tuning, or retraining of existing models.
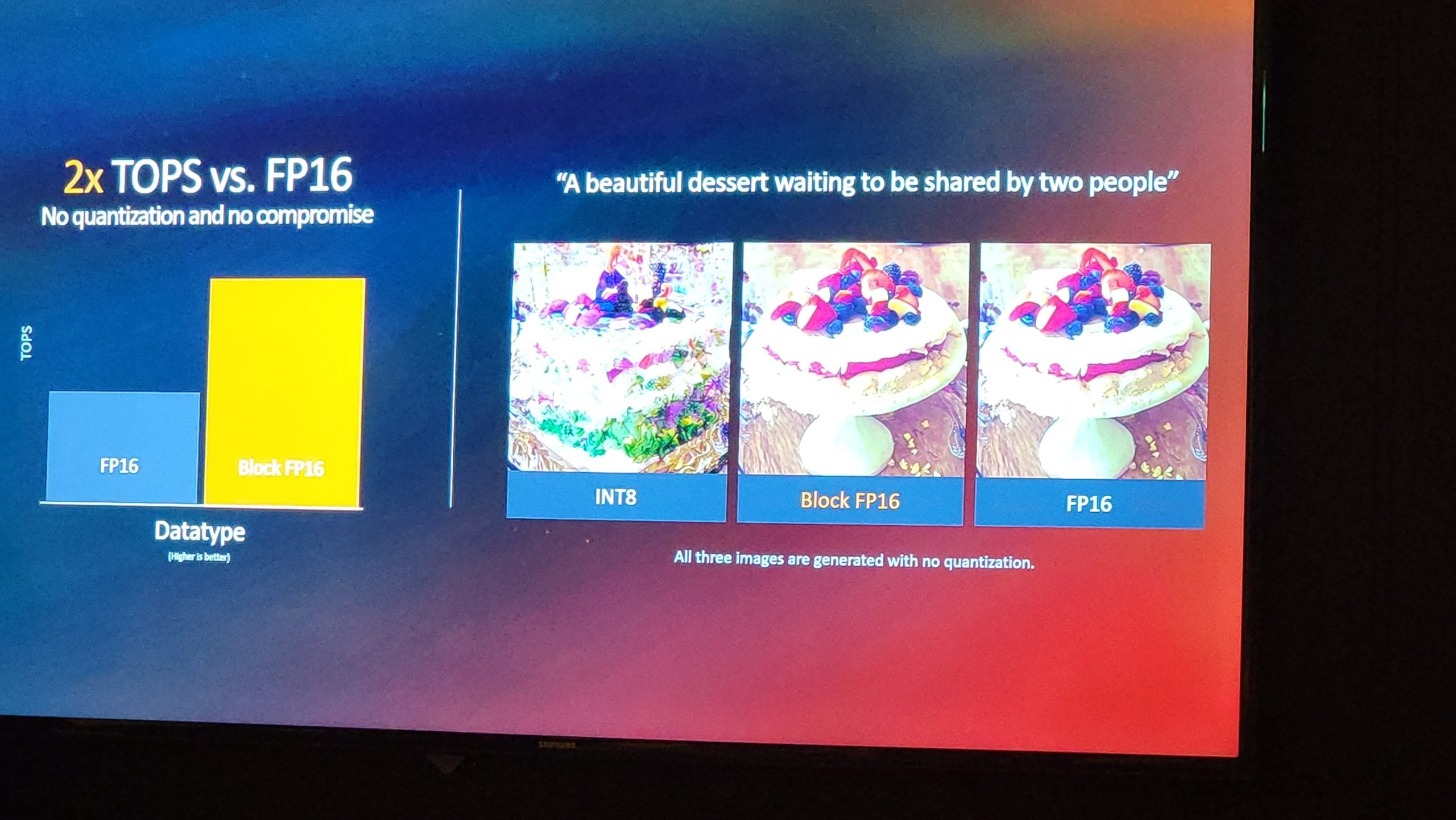
As a matter of fact, the company has the only NPU in the market that supports 50 TOPS with INT8 as well as 50 TOPS with Block FP16. The red team demonstrated a benchmark using both INT8 and Block FP16 to run the same Stable Diffusion prompt to create an image. In this case, a correct image was achieved with Blok FP16. It is not yet clear whether Block FP16 has been approved as an IEEE standard.
Interestingly, AMD made some comparisons with Qualcomm Snapdragon X Elite. Ryzen AI shows notable gains compared to Qualcomm Snapdragon X Elite. AMD’s chip responds 5% faster in GeekBench 6.3.1T. A 10% increase in productivity tasks is claimed, including UL’s Procyon Office benchmark. Cinebench 2024 provides a 30% performance increase in multi-core tests. But none of these numbers are significant or specific to specific datasets/scores/etc. Not supported by.
Sharing many metrics such as productivity, content rendering and multi-threaded performance, AMD also compared the Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 with Intel’s Meteor Lake-based Core Ultra 185H model. ±. Comparing both chips, we see a 4% increase in UL’s Procyon Office tests. On the other hand, while video editing with Adobe Premiere Pro showed a huge increase of 40%, Cinebench 2024 multi-threaded test showed a huge inconsistency of 47%. is being knitted . The most impressive gain published by AMD belongs to 3D rendering processes with Blender. Here, Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 provides a massive 73% performance increase compared to Intel Core Ultra 185H. Again, AMD does not provide any numbers or scores to support this data or the percentages it mentions.
Now let’s look at the game numbers. According to AMD, Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 can offer an average of 36% better performance in selected games compared to Core Ultra 185H. There was a 28% difference in games such as Shadow of the Tomb Raider and a 32% difference in Assassin’s Creed Mirage. We see a 33% increase in Far Cry 6 and a 38% increase in F1 2023.

