What is Wi-Fi 7, What Features Does It Offer?

Devices supported by Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E technology have become widespread in homes and offices. We cannot say that current wireless connection technologies are outdated, but the successor of these standards has already been introduced: Wi-Fi 7.
Wi-Fi 7 is just like previous technologies. It comes with higher data speeds, lower latency, the ability to handle more connected devices, and improves on the current standard with different improvements. Supported products have been around for a while and are becoming more common over time. We started to see Wi-Fi 7 supported modems, routers, mesh systems and motherboards. From now on, new generation smartphones will also be offered with the latest connection technologies.
Wi-Fi Alliance, approved the new standard only in January 2024. On the other hand, some major players in the market had started to release Wi-Fi 7 routers early. As you can guess, the first products offered for sale appeal to the premium class, which means they are very expensive. So we need to ask ourselves a few questions. Is it worth paying the price difference between Wi-Fi6E and Wi-Fi 7? What advantages will those who want Wi-Fi 7 get in a period when the ecosystem is not yet fully established? How long do we have to wait for Wi-Fi 7 supported devices to benefit from the benefits? We will try to answer your questions as much as possible.
If you’re thinking of buying new networking hardware or want to improve your existing connection, Wi-Fi 7 should be on your radar. Prices may be a little expensive at first, but just like other standards, they will become cheaper and more accessible over time. Here’s everything you need to know about the successor to Wi-Fi 6.
What is Wi-Fi 7?
Wi-Fi 7, officially known as 802.11be, builds on the foundation laid by Wi-Fi 6E. This means that it supports 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz wireless bands. However, the Wi-Fi Alliance expects Wi-Fi 7 to deliver higher transfer speeds, reduce latency, and improve overall network capacity compared to Wi-Fi 6E, with various improvements. made it possible to increase it.
To achieve these goals, the maximum channel bandwidth has been doubled from 160 MHz to 320 MHz, while the maximum number of MU-MIMO spatial streams has been increased from 8 to 16. or it turned out. Quadratic amplitude modulation (QAM) is one of the methods used to compress and organize more data into radio signals. While 1024 QAM was implemented in Wi-Fi 6 and 6E, a jump to 4098 (4K) QAM was made with Wi-Fi 7. According to TP-Link, a 20% theoretical data rate improvement was achieved with the switch from 1024 QAM to 4K QAM. Thanks to higher data rates and spectral efficiency, Wi-Fi 7 routers can reliably serve a larger number of wireless devices.
Wi-Fi 7 supports Multi-Link Operation (MLO) technology, which allows routers to connect to a Wi-Fi 7 client using multiple wireless bands and channels simultaneously. For example, a Wi-Fi 7 device can connect to a Wi-Fi 7 router using a single unified connection that combines the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands. This method offers many advantages such as lower latency, higher data speeds, advanced band load balancing and higher network reliability.

With Wi-Fi 6E, a theoretical maximum data rate of 9.6 Gbps could be offered. With all the improvements, Wi-Fi 7 can reach the maximum speed of 46 Gbps. The values we mentioned are on paper, that is, it may not be possible to see these values in the devices we purchase. Still, the potential increase in network throughput compared to Wi-Fi 6E is huge.
Wi-Fi 6 offered only incremental speed gains over Wi-Fi 5. Wi-Fi 7 will be able to provide lightning-fast connections with very high bandwidth. For this reason, there is a nomenclature in the industry such as “802.11be EHT”. The EHT suffix at the end comes from Extremely High Throughput, which means Extremely High Throughput.
Seventh generation Wi-Fi will be backwards compatible like previous standards. However, to benefit from the new features and improved performance offered by 802.11be, devices will need to be Wi-Fi 7 supported. In other words, you need new routers and access points, as well as the smartphones, laptops, TVs, and other devices you connect to.
When Wi-Fi 6 was officially released two years ago, it introduced new features including Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MU-MIMO) and Target Wake Time (TWT). Several new wireless technologies designed to improve overall performance have become available. The same technologies will be available in Wi-Fi 7 with some minor changes.
In summary, OFDMA provides the opportunity for smaller data packets that can be transmitted to more than one user at the same time by dividing the channels into resource units (RU). In this way, latency is reduced and network resources can be used more efficiently.
With MU-MIMO, wireless routers can deliver higher performance for applications such as video streaming and online gaming by using different spatial streams to allow simultaneous data transmission. TWT, on the other hand, helps preserve battery life by ensuring that client devices remain in a sleep state until they need to access the network. The Wi-Fi 7 standard will build on these (and other) existing Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E technologies and introduce several new technologies.
What Does Wi-Fi 7 Offer?
Wi-Fi 7 still uses the same three bands as Wi-Fi 6E: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz. So what is the importance of Wi-Fi 7? It comes with wider channels. Wi-Fi 7 doubles the channel size of the 6 GHz band from 160 MHz to 320 MHz. Think of it as a highway stretching from two lanes to four; That is, the amount of data that can be transmitted at once will increase significantly. According to Intel, one of the companies that produces certified chipsets, a typical Wi-Fi 7 laptop supports 5 Gbps, which is 2.4 times faster than the 2.4 Gbps possible with Wi-Fi 6/6E. It can reach a “maximum potential” of .8 Gbps.
Another important step towards Wi-Fi 7 is Multi-Link Operation (MLO). While Wi-Fi 6 and 6E provided access to multiple bands, devices could only connect to one band at a time. MLO allows Wi-Fi 7 devices to connect to two bands simultaneously. In this way, improved reliability and ultra-low latency times can be achieved along with higher speeds.
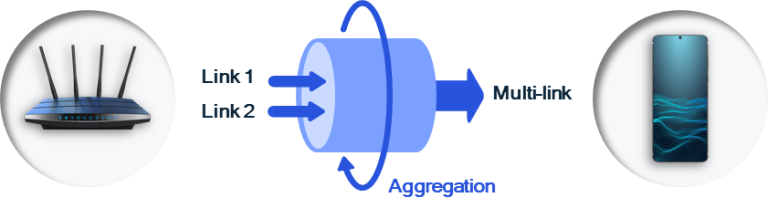
Let’s go back to the highway analogy. In older versions of Wi-Fi, cars could only move in one lane at a time and could switch to a different lane when there was traffic congestion. With MLO, cars will be able to travel on two highways at the same time and avoid slowdowns caused by traffic congestion.
The new standard will offer improved OFDMA operations using Multiple Resource Units (MRUs) designed to further reduce latency and interference. The biggest improvement is the doubling of MU-MIMO streams to 16. This is the key driving force behind why the industry can deliver such large overall efficiency gains compared to Wi-Fi 6.
Additionally, Wi-Fi 7 is expected to come with Restricted Target Wake Time, which allows the router to reserve bandwidth for certain types of data transmission. . The goal is to preserve the battery life of connected devices while optimizing network resources. Let’s take a brief summary of the innovations of Wi-Fi 7:
- Increased Channel Bandwidth: Wi-Fi 7 will offer faster data transmission by doubling the maximum channel bandwidth from 160 MHz to 320 MHz. The larger the MHz range, the more data you can put into it. With this expanded bandwidth, you can experience faster wireless download speeds than ever before. Each band is divided into channels. The 2.4-GHz band consists of 11 channels of 20 megahertz (MHz) each. There are 45 channels in the 5-GHz band, but they can combine to form 40 MHz or 80 MHz channels, as opposed to the 20 MHz limit. The 6-GHz band supports 60 channels, and with Wi-Fi 6E, these channels can expand up to 160 MHz. Wi-Fi 7 will support channels up to 320 MHz width. The wider the channel, the more data it will be able to transmit.
- 4K Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM): Developments on the QAM side will enable each signal to fit up to 120% more data into a channel compared to Wi-Fi 6E. QAM is a method used to transmit and receive data on radio frequency waves. The higher it is, the more information you can collect. While Wi-Fi 7 offered 4K-QAM support, Wi-Fi 6 was limited to 1.024-QAM and Wi-Fi 5 was limited to 256-QAM. As a result, as QAM increases, range decreases and you need a stronger signal.
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO): This feature will increase speed and stability by allowing devices to spread connections across two or three bands (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz). If one band is out of range, the device will be able to seamlessly switch to the other without needing to reconnect. This is perhaps the most exciting development in Wi-Fi 7. MLO is able to combine various frequencies across bands into a single connection. A Wi-Fi 7 router can connect to a Wi-Fi 7 device over two or more channels on different bands simultaneously. MLO provides wider channels that can potentially transmit more data. Speed is not always a priority, but MLO also provides more efficient performance. A Wi-Fi 7 router can take into account congestion and other interference and transmit data by choosing the best channel to overcome these problems. Thus, a stable connection is ensured and low latency is maintained.
- Improved Latency: Integration of the entire inner band increases the possibility of instant transmission of data packets by reducing the transportation time constraint. These advances are especially useful for applications that require low latency, such as online gaming and video conferencing.
- MU-MIMO Enhancement: Wi-Fi 7 supports more multi-user, multi-input, multi-output (MU-MIMO) spatial streaming. In other words, routers are enabled to communicate with more devices at the same time. Efficiency and stability will increase, especially in environments where many people are connected to the network.
- Multi Resource Unit (RU): In legacy Wi-Fi 6/6E and earlier versions, when part of a high-speed channel is used by another device, the entire channel is unavailable. tiring. With Wi-Fi 7, channels can be shared if there is free space.
- Compressed Blocks: Reduced additional communication load with 512-compressed block structure.
In summary, it is faster, more reliable, can maintain low-latency performance, is more efficient and offers a more stable connection with more devices. With these advantages, we can say that wireless connection technologies have come a little closer to wired connections. The experience will improve, especially in online games and cloud-based games. Wi-Fi 7 also combats congestion and interference, bringing tangible benefits to areas where devices are dense or where neighboring networks overlap. The improved connection experience provided in crowded environments is much more important, especially for companies, large venues and open areas.
When Will It Be Available?
Wi-Fi 7 devices and routers begin to hit the market in early 2023. You won’t feel the benefits of the new standard until you use supported devices. The good thing is that Wi-Fi 7 routers are backwards compatible. In other words, products that benefit from the new standard can be purchased as an investment for the future.
On the device side, we are starting to see smartphones and laptops with Wi-Fi 7. All major chipmakers, including Qualcomm, Intel, Broadcom and MediaTek, now offer Wi-Fi 7 certified chipsets. It is also said that more than 233 million Wi-Fi 7 devices will enter the market in 2024.
Switching to Wi-Fi 7?
Wi-Fi 7 is a significant upgrade that offers improvements in several aspects compared to Wi-Fi 6E. Higher throughput, lower latency, increased capacity and higher main Carrier speeds (for network systems) are offered. On the other hand, many router manufacturers are combining these Wi-Fi 7 improvements with hardware-level goodies like faster multi-core SoCs and 10Gbps LAN/WAN ports. It is dying.
What we really need to think about is the costs. Currently, the price of Wi-Fi supported network products is very expensive. All those who bought these routers early at high prices, primarily wanted the highest possible performance and wanted to be ready from day one when Wi-Fi 7 products hit the market. like people.

The driver/software requirements to have a fully functional Wi-Fi 7 network are not yet fully ready. Yes, Wi-Fi 7 is available, but there is some more time for the market to fully adopt the new standard. You can expect things to get back on track at least by the end of 2024 and the beginning of 2025. If you say no, I have the required budget, the supported device and want high performance, you can switch.
Is Wi-Fi 7 Compatible with Older Devices?
Yes, it is compatible. All your existing laptops, smartphones and TVs will continue to work with the Wi-Fi 7 router as they did until now.
What is Required to Use?
To use Wi-Fi 7, you need at least a Wi-Fi 7 router and a Wi-Fi 7-enabled device. However, you can continue to use your old hardware with a new Wi-Fi 7 router.
Which Apps Support Wi-Fi 7?
All your existing apps will work just fine with Wi-Fi 7. Augmented, virtual and extended reality (AR/VR/XR) applications, immersive 3D education and ultra-high-definition (8K) video streaming In newer, higher-level programs such as business You will need Wi-Fi 7. To get the most out of these technologies, you’ll need Wi-Fi 7.
Does Wi-Fi 7 Provide Benefits in Old Applications?
Yes, it can be useful depending on the situation. For example, built-in multi-connectivity that allows devices to send and receive data over all three bands (2.4GHz, 5GHz, or 6GHz). thanks to you It can switch between or combine them as needed to provide the best possible speed. This way, if your downstairs neighbor’s kids start watching 4K video on three separate TVs at the same time, your network will automatically adjust to make the most of the available network space.
Will We See the Benefits of Wi-Fi 7 Supported Devices?
Regardless of whether it is a smartphone or other device, the Wi-Fi 7 supported products you have purchased do not mean anything on their own. Unless you use a network device that works with Wi-Fi 7, you cannot benefit from all the benefits of Wi-Fi 7.
Can We Add Wi-Fi 7 Support to an Unsupported Computer?
This is possible. You will need a free PCIe NGFF 2230 M.2 slot on your computer. You can plug the Intel BE200 Wi-Fi 7 adapter, which costs about $40, into this slot. Your computer must also be running Linux or Windows and have an Intel processor.
Wi-Fi 7 Supported Smartphones
- ASUS ROG Phone 7
- ASUS ROG Phone 8
- ASUS ROG Phone 8 Pro
- ASUS Zenfone 10
- ASUS Zenfone 11 Ultra
- Google Pixel 8
- Google Pixel 8 Pro
- Motorola Edge 50 Ultra
- Motorola Edge+
- Nubia Z50S Pro
- OnePlus 12
- OnePlus 12R
- OnePlus Ace 3
- OnePlus Open
- Samsung Galaxy S23 Ultra (Disabled in firmware)
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra
- Samsung Galaxy Z Fold 5 (Disabled in firmware)
- Vivo X Fold 3
- Vivo X Fold 3 Pro
- Vivo X100
- Vivo X100 Pro
- Vivo X100 Ultra
- Vivo X100s
- Vivo X100s Pro
- ZTE nubia Red Magic 9 Pro
- ZTE nubia Red Magic 9 Pro+
- ZTE nubia Z60 Ultra
- Xiaomi 13T Pro
- Xiaomi 14
- Xiaomi 14 Pro
- Xiaomi 14 Ultra
- Xiaomi Mix Fold 3
- Redmi K70
- Redmi K70 Pro
- realme GT5
- realme GT5 Pro
- Meizu 21
- Honor Magic 5
- Honor Magic 5 Pro
- Honor Magic 5 Ultimate
- Honor Magic 6
- Honor Magic 6 Pro
- Oppo Find X7 Ultra
- Oppo Find X6
- Oppo Find X6 Pro
- OnePlus 11
- OnePlus Ace 2 Pro
On the Apple side iPhone 16 Pro and iPhone 16 Pro Max models are expected to come with Wi-Fi 7 support. In addition, Android devices such as the Pixel 9 series, Google Pixel 8a, Samsung Galaxy Z Flip 6, Samsung Galaxy Z Fold 6 (potentially Samsung Galaxy Z Fold 6 Ultra) and OnePlus Open 2 will come with Wi-Fi 7 support. .
Additionally, although some devices are equipped to support Wi-Fi 7, they will need driver/firmware/software updates to fully enable it at a later date.

