What is PWM? What is the Difference Between 3-Pin DC and 4-Pin PWM Fans?
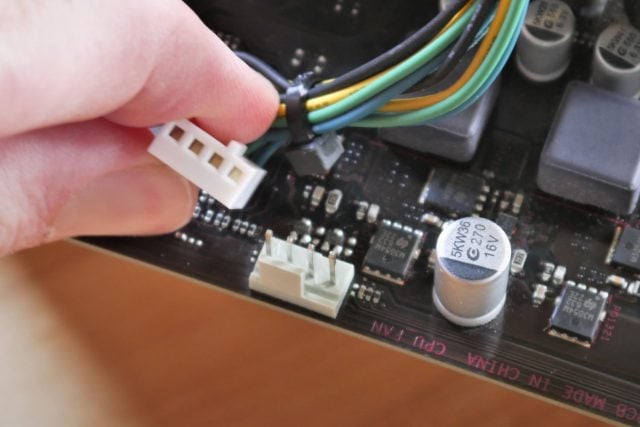

You have seen the term, abbreviated as PWM, in the descriptions of cases and coolers, as well as in the motherboard BIOS and some software. So what does PWM mean? What advantages does it offer?
A PWM type fan or pump has the ability to quickly modulate the pulse signal, providing control depending on the instantaneous requirements of the system. Fans of this type move depending on the temperature curves set by the motherboard, controller or operating system. Fan blades accelerate and slow down depending on the current situation. In other words, it is useful because it provides full control over the fans.
The same goes for assisted pumps, which can change the speed of the motor by taking into account component or fluid temperatures. You may not see this support in models released years ago, but most motherboards released recently offer support for PWM fans (4-pin headers).
What is PWM?
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation), used in various fields from electronics to PC hardware, means pulse width modulation. Modulation, which is an integral part of PC cooling systems, is essentially a technology that provides dynamic control over fans.
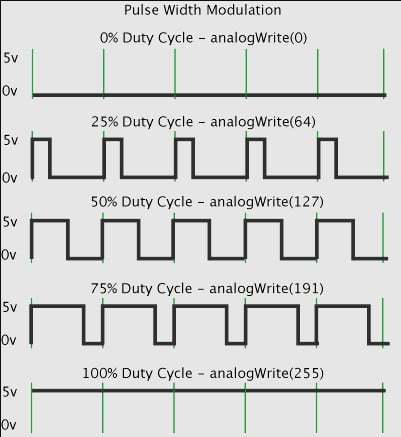
Unlike standard DC fans, these fans can automatically adjust their speed depending on the temperature. When the temperatures are at normal values, the fans operate at lower speeds, thus producing more noise and higher power consumption (always lower). It does not consume much power) and is prevented. PWM technology is advantageous in every way. The downside is that fans are more expensive and require a motherboard with a special PWM supported header.

PWM fans and/or pumps are found in some CPU coolers and graphics card coolers. Let’s also add that it is used in servo motors, voltage regulation, telecommunications and audio equipment.
How does it work?
Pulse Width Modulation actually allows us to control the RPM, that is, the rotation speed, of a fan. If a fan can run at 3000 RPM and we want it to run at its maximum speed, we set the duty cycle to 100%. If we want to save power and run the fans at half their maximum speed, we can set the duty cycle to 50%. In this case, the fan operates at half its capacity, that is, we reduce its speed to 1500 RPM.

An integrated circuit is used to control the speed of a fan or pump and therefore how much cooling it provides to the CPU or GPU. PWM fans and pumps can change their speed and airflow depending on the temperature of the component. PWM works like a switch, turning it on and off while controlling the level of power delivered to the fan or pump. PWM fans work in conjunction with the motor, receiving full power or zero power.
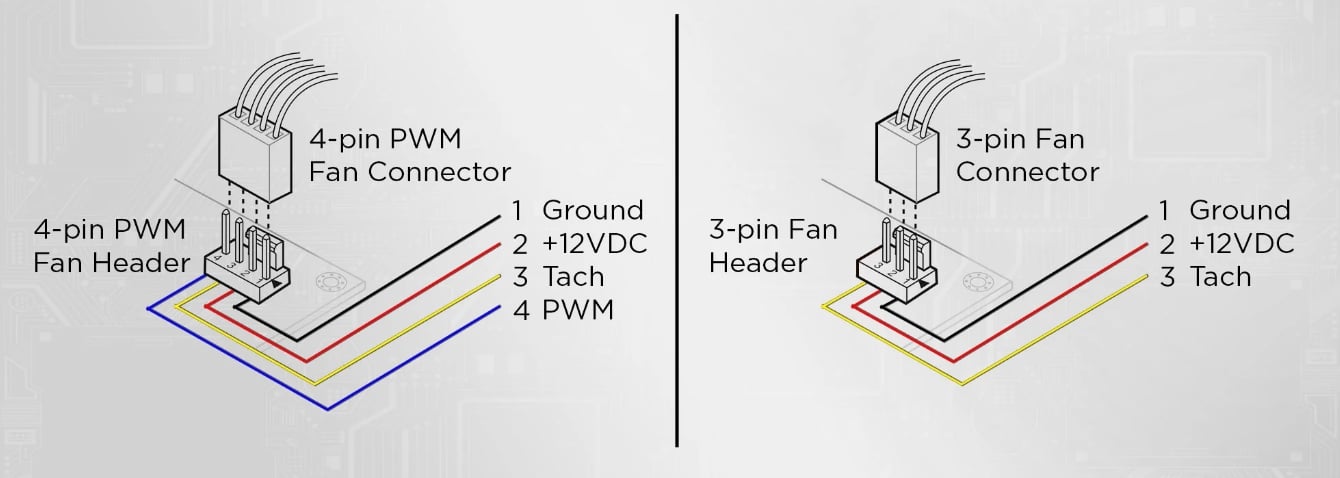
What is 4-Pin PWM Connection?
4-pin PWM is a type of connector commonly used to connect PWM fans to a power supply, motherboard, or a fan controller. Usually, the cable coming from the fan is plugged into the 4-pin header on the motherboard and allows users to access the PWM features of their systems. The function of 4 separate pins is as follows:
- Ground (GND): This pin provides the electrical ground connection, which serves as the reference point for the electrical circuit.
- +12V (VCC): +12V connection provides the fan with a constant 12 volt power supply, providing the energy required for its operation.
- Sense-Tach (S): This pin monitors the rotation speed of the fan, allowing the motherboard or controller to receive feedback on how fast the fan is spinning.
- PWM(P): This pin is responsible for transmitting the PWM signal. It carries the modulated signal that controls the speed of the fan by adjusting the duty cycle.
PWM vs. DC: Which One Should Be Preferred?
When it comes to choosing a fan for your computer, there are two options: One is PWM, which we explained, and the other is direct current. DC (direct current) fans. Direct current fans cannot calculate how much power must be converted into movement of the blades and draw power directly from the source. It is possible to change the speed of DC fans by changing the amount of power supplied to the fan. We can make adjustments on most motherboards, but it is still not possible to make as fine adjustments as a PWM circuit.
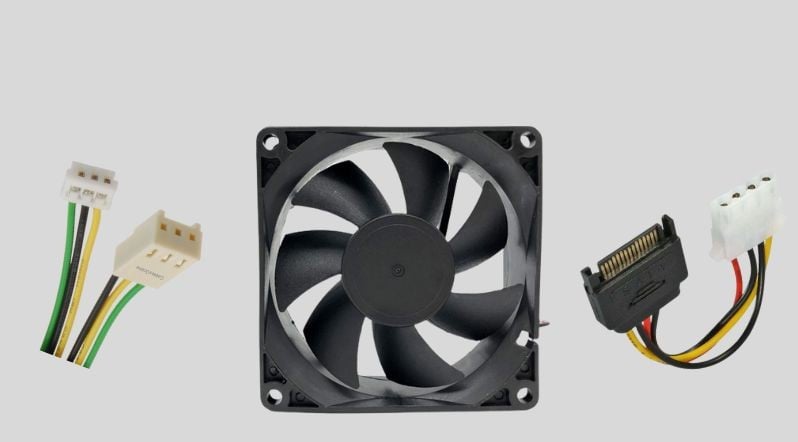
A DC fan or pump has only three pins compared to the four pins on the PWM component. The missing fourth wire allows input to the PWM circuit, which allows the system to use square waves of high-frequency current to determine whether the motor turns on or off. ⎠⎠⎠) allows it to be sent. When the fan is in motion, this signal wave changes rapidly between on and off states. The human ear cannot perceive anything other than the sound of the blades moving the air inside the case.
Since the supply voltage is constant throughout use and PWM signals control the speed of the device, there are important differences in terms of precise control. PWM fans operate without stopping the motor. Thin may spin slower than DC fans, but PWM fans generally consume more power.
In summary, PWM fans are better and provide more control. PWM is a dynamic technique that controls various aspects such as fan speed and RGB lighting. Supported components can dynamically adjust their speed based on factors such as cooling requirements, ambient temperature, and noise preferences.
| PWM Fan | DC Fan |
|---|---|
| Precise speed control via PWM signal, adjusting the duty cycle for various speeds. | Limited speed control via voltage adjustments; usually uses resistors or hardware switches. |
| A wide speed range can be achieved, from very low revs to very high revs. | Limited speed range; It may not reach speeds as high or low as PWM fans. |
| More efficient in terms of energy consumption and noise reduction at low speeds. | It is less efficient and can produce more noise at low voltages due to lower power. |
| Generally compatible with PWM headers on motherboards and fan controllers. | Can be connected to standard 3-pin fan headers on motherboards or fan controllers. |
| It can dynamically adjust fan speeds according to temperature changes for optimum cooling. | Limited to static speed settings based on voltage input. |
| Ideal for situations requiring precise speed control, quiet operation and dynamic thermal management. | Suitable for basic cooling needs where constant speed operation is acceptable. |
No PWM Support?
If your motherboard only has 3-pin fan headers, it means there is no PWM support. There is no point in paying more for more expensive 4-pin fans since the PWM function will be useless. Also, the same thing applies if you are going to run the fans at high RPM all the time. You don’t need precise control of PWM fans.
If your motherboard has 4-pin fan headers and your goal is to achieve precise fan RPMs that increase and decrease depending on the temperature of your CPU (or other sensors) Buy 4-pin PWM fans.
If your budget is limited and you don’t want to invest in 4-pin fans, most modern motherboards have a feature called voltage regulation. This function limits the voltage supply to the fan headers and allows the speed of the 3-pin fans to be changed. Of course, there is no sensitivity like in PWM.
Can 3-Pin Fans Be Connected to 4-Pin Headers?
Yes, you can wear it. The system will detect the connected cooler as a DC component and operate it accordingly. In a computer not all fans are usually PWM, a mix of both DC and PWM fans are used. CPU and GPU coolers are usually PWM type.
In fact, both fans are sufficient to properly cool the computer, depending on maximum speeds and air flow. The only difference is that DC fans do not offer precise control compared to PWM fans. This is also important for most people in terms of noise level.
Do Laptops Use PWM Fans?
Yes, although laptops have weaker cooling systems compared to desktop computers, PWM fans are used.
Do 3-Pin Fans Create Noise?
Yes, but this varies depending on the fan. Larger fans operate at lower RPM (rotations per minute) than smaller fans. to make the air quieter in general It tends to tangle. However, a 3-Pin fan produces loud noise because it will always run at full RPM or intensity.
The only way to reduce this disadvantage is to find a suitable 3-pin fan that operates quietly. If you don’t have access to fan controls, choose a good fan. If you want to build a quiet system, it’s best to use PWM fans and PWM fan control hubs.

