AMD Zen 5 on Stage: Ryzen 9000 Series Features

AMD CEO Lisa Su introduced the company’s new generation Ryzen processors in the Computex 2024 keynote speech. During the presentation, chips used in different areas, including mobile, server and desktop platforms, were introduced. Now let’s look at all the details of the Ryzen 9000 ‘Granite Ridge’ processors that come with the Zen 5 microarchitecture and will replace the Ryzen 7000 series.
There are four new CPUs in the red team’s Zen 5 desktop product portfolio. Ryzen 9 9950X, which comes with 16 CPU cores and a maximum boost frequency of 5.7 GHz, will lead the flagship model. After the flagship, 6, 8 and 12 core models come in the same way. These are all “X series” chips, meaning they have unlocked multipliers and higher TDP and clock speeds.
Along with other improvements, AMD claims that its new flagship Ryzen 9 9950X outperforms rival flagship Raptor Lake Refresh by an average of 11% in gaming and 21% in productivity workloads. However, let us remind you that the newly introduced Granite Ridge chips will compete with the upcoming Intel Arrow Lake. The chips can also offer up to twice as high performance in artificial intelligence and AVX-512 workloads.
We will talk about the details in a moment, but let’s go over it briefly. Regarding performance, AMD states that the Zen 5 architecture provides an average of 16% IPC increase. The turbo clock speeds of the new desktop Ryzen chips remain the same as the Ryzen 7000 series. This means that we can expect similar performance gains in all models, from three to five.
AM5 socket support continues with the Ryzen 9000 series. If you remember, AMD switched to the AM5 platform for the first time with Ryzen 7000. With the new series, two new chipsets, X870E (Extreme) and X870, are also available. No information was given about the basic features that vendors would integrate into their motherboards. We will soon open a parenthesis specifically for motherboards. We know that USB 4.0 ports are standard on the
Now let’s look at the first details of the Zen 5 architecture and the features of the chips in the Ryzen 9000 series.
AMD Ryzen 9000 Series Features
Let us state from the outset that despite having the same number of cores, frequencies and cache capacities as the previous generation Ryzen 7000 models, significant performance improvements are provided. There are significant generation-to-generation TDP declines in the three models. In other words, power efficiency has increased. AMD cites doubling cache data bandwidth among the improvements that significantly increase gaming performance. Red team Zen 5 Ryzen 9000 series delivers significantly more performance than its Zen 4 predecessors, with much lower power consumption It speaks for itself.
This time, we did not see claims such as “the world’s fastest game processor” in the presentation. In other words, we can say that the Ryzen 7000X3D series, optimized for gaming, will continue to dominate the top of the gaming lists, at least until the 3D V-Cache supported Ryzen 9000X3D models arrive.
Ryzen 9 9950X, the flagship SKU, has 16 cores, up to 5.7GHz max overclock clock, 64MB L3 and 16MB L2 (1MB per L2 core) cache It has a split 80 MB cache and 170W TDP. Ryzen 9 9900X comes with 12 cores, maximum boost clock up to 5.6 GHz, 64 MB L3 cache and 120W TDP.
When we scroll down we see the 9700X. Ryzen 7 9700X was introduced with 8 cores, maximum boost clock up to 5.5 GHz, 32 MB L3 cache and 65W TDP. Finally, there is the entry-intermediate level. Ryzen 5 9600X will have only 6 cores, a maximum boost clock of up to 5.4 GHz, 32 MB L3 cache and 65W TDP.
| Architectural | core | P-Core Frequency | E-Core Frequency | Cache (L2/L3) | TDP/PBP/MTP | Memory Dest. |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 9 7950X3D | Zen 4 | 16 / 32 | 4.2 / 5.7 | 144MB (16+128) | 120W/162W | DDR5-5200 | |
| Core i9-14900K/KF | Raptor Lake Refresh | 24 / 32 (8+16) | 3.2/6.0 | <2.4/4.4 | 68MB (32+36) | 125W/253W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-5600 |
| Ryzen 9 9950X | Zen 5 | 16 / 32 | 4.3/5.7 | 80MB (16+64) | 170W/230W | DDR5-5600 | |
| Ryzen 9 7950X | Zen 4 | 16 / 32 | 4.5 / 5.7 | 80MB (16+64) | 170W/230W | DDR5-5200 | |
| Ryzen 9 7900X3D | Zen 4 | 12/24 | 4.4 / 5.6 | 140MB (12+128) | 120W/162W | DDR5-5200 | |
| Ryzen 9 9900X | Zen 5 | 12/24 | 4.4 / 5.6 | 76MB (12+64) | 120W/162W | DDR5-5600 | |
| Ryzen 9 7900X | Zen 4 | 12/24 | 4.7 / 5.6 | 76MB (12+64) | 170W/230W | DDR5-5200 | |
| Core i7-14700K/KF | Raptor Lake Refresh | 20 / 28 (8+12) | 3.4/5.6 | 2.5 / 4.3 | 61MB (28+33) | 125W/253W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-5600 |
| Ryzen 7 7800X3D | Zen 4 | 8 /16 | 4.2 / 5.0 | 104MB (8+96) | 120W/162W | DDR5-5200 | |
| Ryzen 7 9700X | Zen 5 | 8 /16 | 3.8/5.5 | 40MB (8+32) | 65W/88W | DDR5-5600 | |
| Ryzen 7 7700X | Zen 4 | 8 /16 | 4.5 / 5.4 | 40MB (8+32) | 105W/142W | DDR5-5200 | |
| Core i5-14600K/KF | Raptor Lake Refresh | 14 / 20 (6+8) | 3.5 / 5.3 | 2.6/4.0 | 44MB (20+24) | 125W/181W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-5600 |
| Ryzen 5 9600X | Zen 5 | 6 / 12 | 3.9/5.4 | 38MB (6+32) | 65W/88W | DDR5-5600 | |
| Ryzen 5 7600X | Zen 4 | 6 / 12 | 4.7/5.3 | 38MB (6+32) | 105W/142W | DDR5-5200 |
RAM Support
Ryzen 9000 chips will have similar memory support as the previous generation. However, the maximum support increased to DDR5-5600. AMD states that future X870E and X870 motherboard chipsets will allow faster EXPO memory profiles than seen in Zen 4. JEDEC memory features of the four introduced Ryzen 9000 chips were not disclosed. We hope to learn more before the launch of the Ryzen 9000 family in July 2024. According to product pages that AMD has released since the keynote, the Ryzen 9000 family is available through JEDEC for in-warranty configurations. DDR5-5600 It will offer memory support.
What Does Zen 5 Architecture Offer?
Zen 5 marks AMD’s latest advancement in the Ryzen microarchitecture. The company has not disclosed many details yet, but we will try to provide you with all the available information. AMD says Zen 5 represents a complete overhaul of the architecture, delivering a 16% increase in IPC. Let’s start with transaction technologies.
AMD did not share the details of the production technology it uses, but we know that the chips will be built on the TSMC 4nm process. If you remember, the Ryzen 7000 series was built on the 5nm (N5) technique. Although no details are given, we estimate that Ryzen 9000 is developed with TSMC N4P. N4P can provide 11% more performance, 22% higher power efficiency and 6% higher transistor density (optical shrinkage) compared to TSMC N5 technology.
TSMC says that this process uses 6% fewer masks for production due to the increased number of EUV layers, which is more cost-effective. TSMC also noted that N4P is technically part of the 5nm family, so the design rules are compatible and has accelerated deployment for those already using N5. He stated that they did.
The Reds shared only the general outlines of the Zen 5 architecture. The block diagram shows that it is built on the same core compute die (CCD) architecture as the previous generation, with a maximum of eight cores and a large central 32 MB shared L3 complex. It shows. As expected, the chips have the same basic physical design and use the same 6nm I/O die (IOD). Therefore, we expect the graphics support and basic connection options to be the same.
The company says that the frequency residence time (staying at the boost frequency) has increased in Zen 5 chips due to the efficiency of the integrated heat spreader (IHS) design and This shows that some improvements have been made in the thermal design.
The kernel microarchitecture has seen various improvements; AMD points to L2 and L1 caches and doubling data bandwidth from L1 to floating point as a contributing factor to generation-to-generation gains in gaming performance. This makes sense, since latency greatly affects gaming performance.
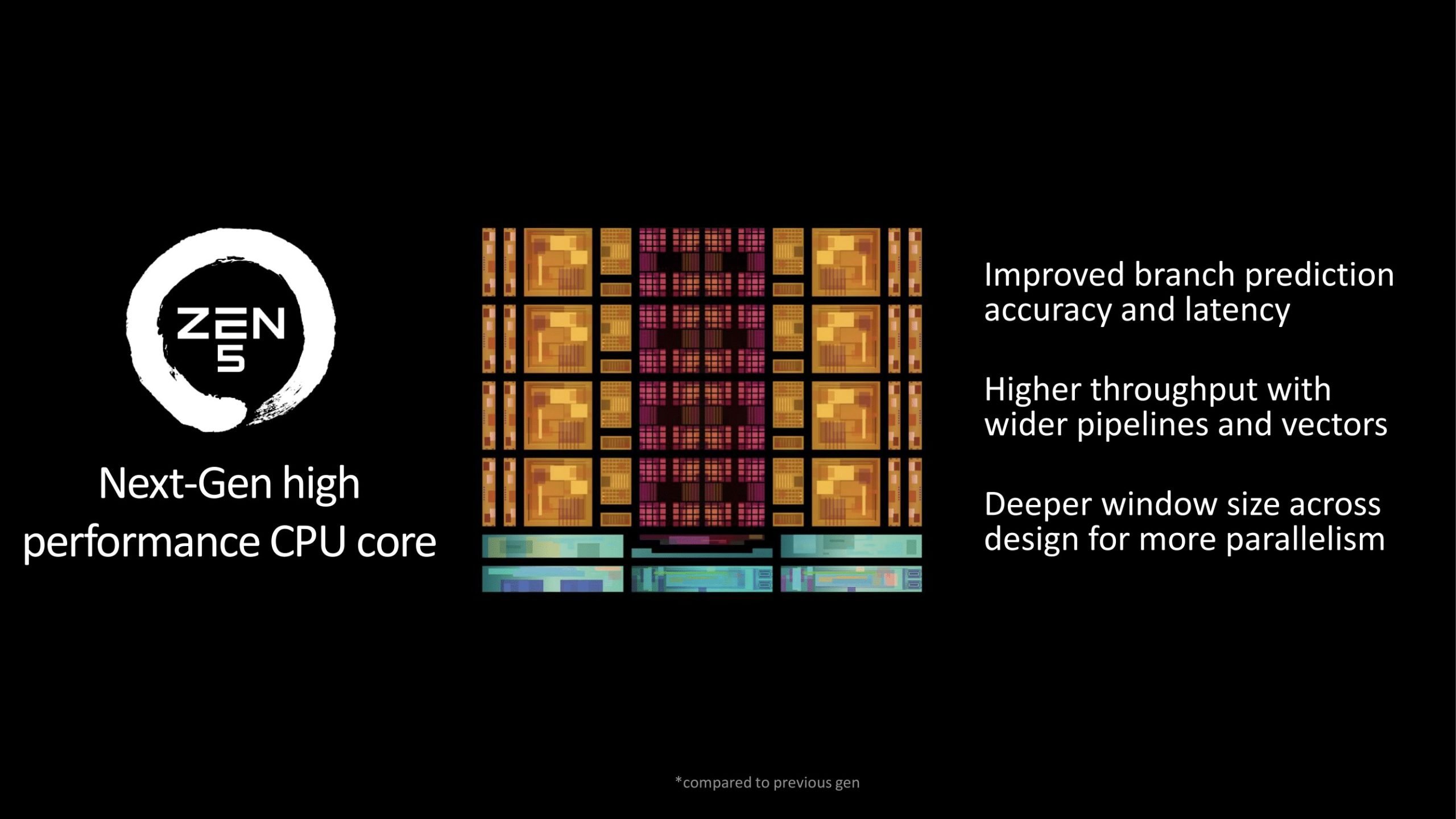
As for other improvements, improved branch prediction accuracy and improved latency to help prevent failed pipeline stages and stalls their duration is mentioned. Zen 5 also includes front end instructions It offers doubled instruction bandwidth for , which is a good improvement along with improved branch prediction.

AMD states that higher efficiency is achieved with wider pipelines and vectors. While attention is being drawn to AVX-512 support, the dual-issue AVX-512 pipeline is no longer used, due to its impact on die space while providing many of the performance advantages of AVX-512. It is stated that he gave an AVX-256 command twice to avoid it. Which seems logical considering that AMD has stated that the throughput of AVX-512 and VNNI (AI command) has doubled. It is possible that it has an AVX-512 processing line. The architecture also features a deeper window size throughout the design for greater parallelism.
It says it offers better AI performance in red team inference and AVX-512 workloads. Notably, AMD’s AVX-512 support in Zen 4 was implemented using 256-bit SIMD over 2 cycles. With Zen 5, AVX-512 SIMDs have been expanded to a full 512 bits, meaning a twofold increase.
| Zen 5 (2024) | Zen 4 (2022) | Zen 3 (2020) | Zen 2 (2019) | Zen 1 (2017) | |
| IPC Development | +16% | +13% | +19% | +15% | +52% |
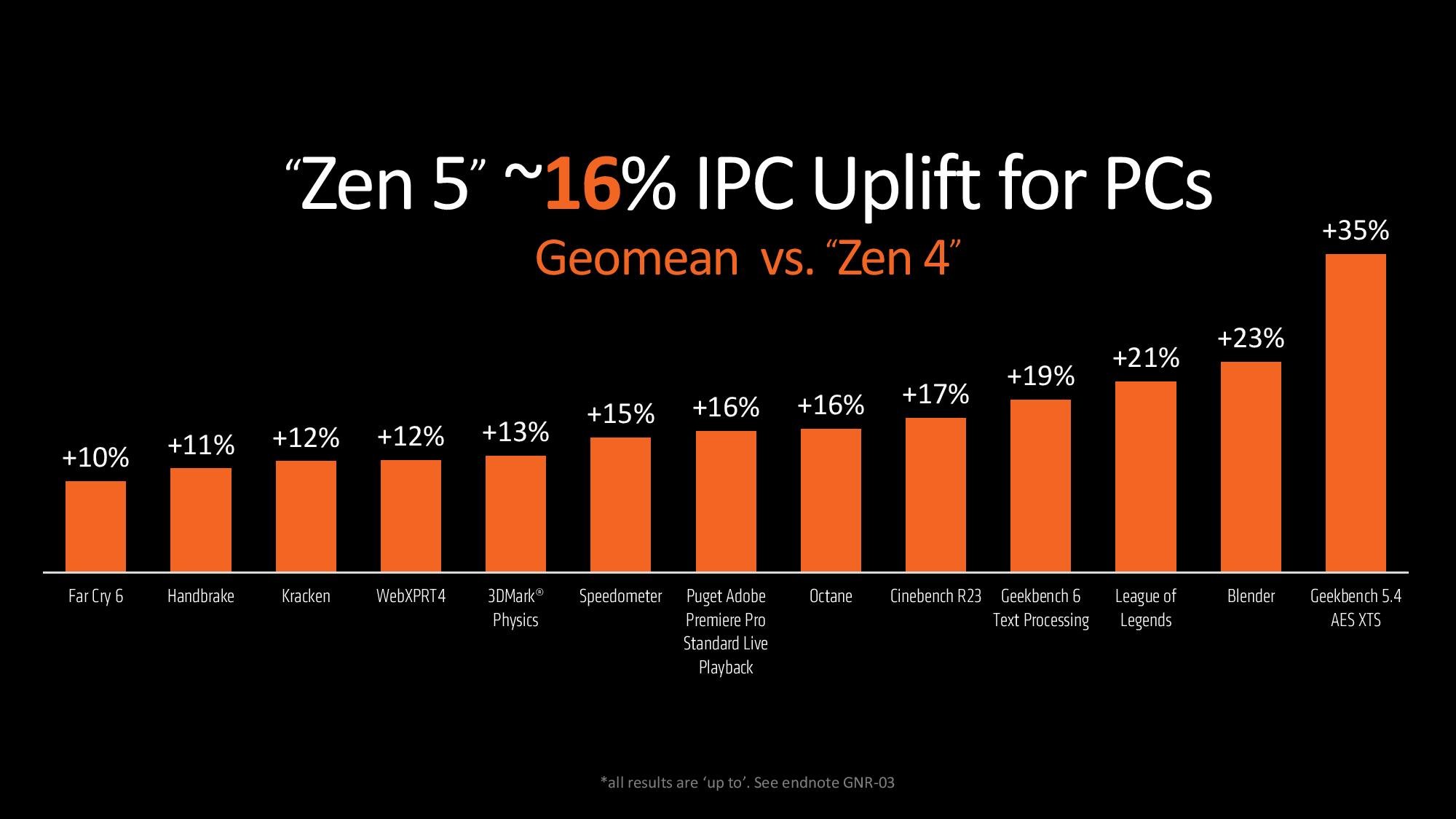
The chip manufacturer has been developing its Zen architecture since 2017. With the first Zen chips, a huge improvement of 52% was achieved compared to Bulldozer. We saw a 13% improvement in the transition from Zen 3 to Zen 4. Zen 5 architecture promises greater things with a 16% jump. IPC increase was measured by taking the geometric mean of 13 separate workloads. This includes games that are not used for older Zen architectures.
AMD claims to achieve a gain of between 10% and 35% in tests. The 35% increase in the Geekbench 5.4 AES XTS test is remarkable. Taking advantage of the VAES512 and VAES256 extensions of the AVX-512 instruction set, Geekbench has recorded a huge performance jump. As a result, AMD’s AVX-512 SIMD changes greatly impact this benchmark in particular (but not only).
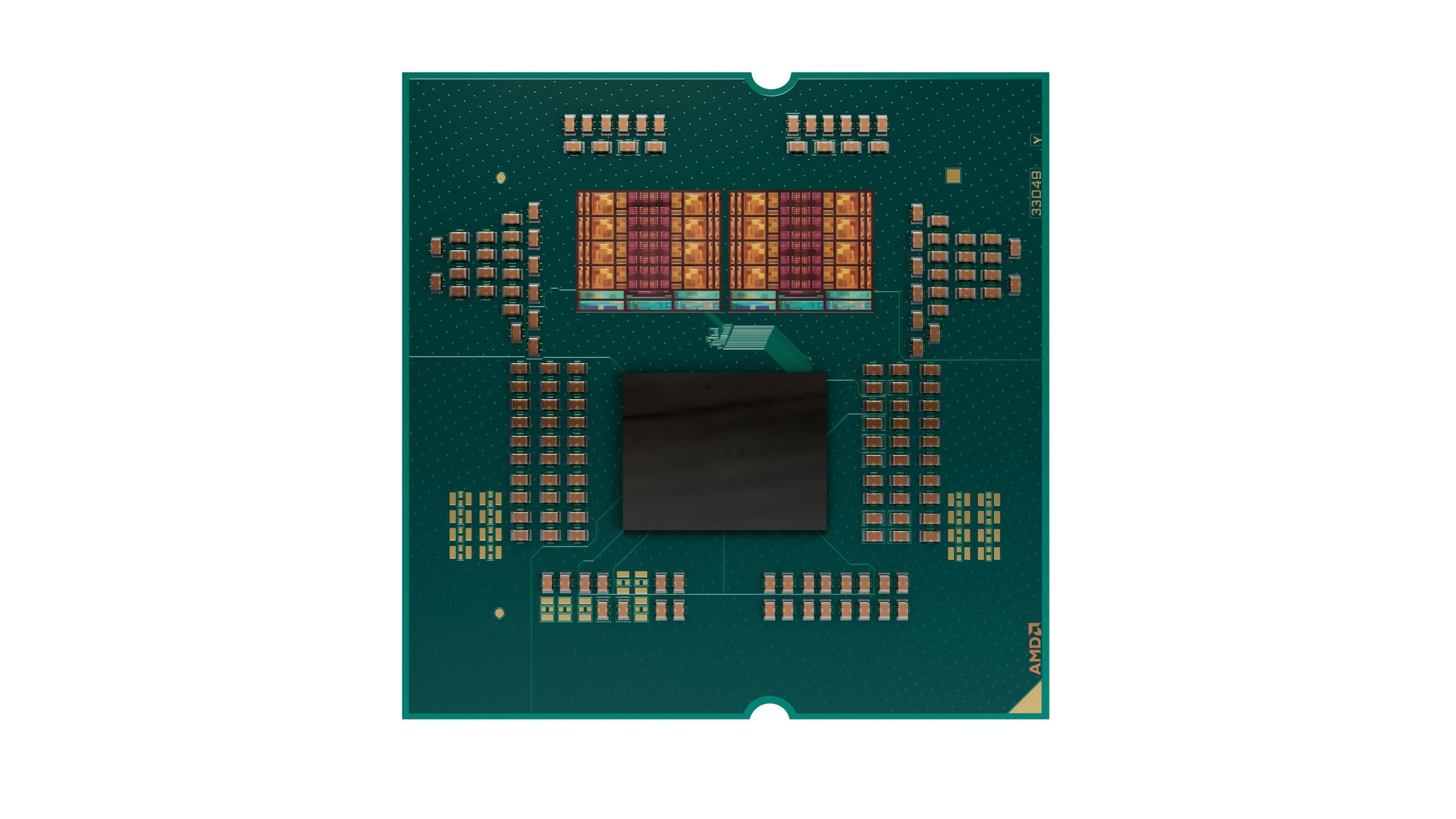
The photo is just above, showing the composition and arrangement of silicon in a Ryzen 9000 series chip with two core complex dies (CCD). As with previous generation Ryzen processors, there is a large central I/O die (IOD) to which all I/O and memory operations are routed. As for CCDs, each die contains the same 8 CPU cores, and AMD equips its Ryzen chips with 1 or 2 CCDs depending on the model. As we said, the new Zen 5 CCDs are produced on one of TSMC’s 4nm processes.
Ryzen 9000 Series Performance
Ryzen 9 9950X vs Intel’s 14th Gen Core i9-14900K. If we look at productivity and content creation workloads; We see a difference of 7% in Procyon Office, 10% in Puget Photoshop and 21% in Cinebench R24 nT. More importantly, there is a 55% performance difference in Handbrake and 56% in Blender.
Interestingly, gaming data shows marginal gains in some games, while highlighting more significant increases in others. AMD’s internal testing reveals that the Ryzen 9 9950X outperforms the Intel Core i9-14900K by 4% in Borderlands 3, 6% in Hitman 3, and 13% in Cyberpunk 2077. On the other hand, there is a difference of 16% in F1 2023, 17% in DOTA 2 and 23% in Horizon Zero Dawn.
In summary, AMD expects the Ryzen 9 9950X to outperform the Core i9-14900K in both productivity workloads (7% to 56%) and gaming workloads (4% to 23%). He says it’s slightly faster. This means a 21% gain in productivity and an 11% gain in gaming. As we always say, it is necessary to approach the tests conducted by the companies with some distance and wait for independent tests.
Let’s continue with artificial intelligence. The company says the Ryzen 9 9950X is 20% faster than the Core i9-14900K in AI workloads and 100% faster when using both a direct-to-CPU PCIe 5.0 SSD and a PCIe 5.0 GPU. It says that it offers PCIe 5.0 efficiency. Yes, this is a bit of a strange claim. There aren’t any PCIe 5.0 GPUs on the market yet, but AMD says supported cards will be coming ‘soon’.
Ryzen 9000 Series Release Date and Price
AMD says that it will launch the Zen 5-supported Ryzen 9000 series processors and the Ryzen 5000XT series, which brings the AM4 platform to life, in July. So, even though the promotion has been made, sales will start later. As for pricing, we did not see any pricing information at the time of the announcement. We will share price information with you soon.
AM5 Support and 800 Series Motherboards
As we mentioned before, AMD is determined to keep the AM5 socket long-lasting. At the very least, they want to provide support for much longer periods of time than other manufacturers offer with their CPU launches and updates. Ryzen 9000 CPUs will also continue to run on the AM5 platform. The new chips are fully backwards compatible with existing 600 series motherboards. BIOS updates will be sufficient to use it.
However, AMD has prepared two new 800 series motherboard chipsets for the launch of Zen 5 on desktop computers. The X870E (Extreme) and X870 chipsets will be included in many new motherboards and we will see numerous models at Computex.

AMD offered only a few details about the X870E and X870 chipsets. What is particularly noteworthy is that USB 4.0 support, which is optional on X670(E) series motherboards, will be offered as standard on all X870(E) motherboards. X870(E) motherboards will also have Wi-Fi 7 support (the 600 series had 6E support) and at least one PCIe 5.0 NVMe slot will continue to be mandatory. The company also notes that motherboards based on both platforms “have a total of 44 PCIe lanes,” split into 24 lanes from the CPU and 20 lanes from the chipset.
Even though the X870 chipsets have arrived, we have not yet seen the more affordable B and A series. We expect low-budget motherboards to hit the market in a few months.
| X870E | x870 | X670E | X670 | B650E | |
| CPU PCIe (PCIe) | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| CPU PCIe (M.2 Slot) | At least 1 PCIe 5.0 Slot | ||||
| Total CPU PCIe Lanes | 24 | ||||
| Chipset PCIe Lanes (Maximum) | 4.0:12 3.0:8 |
4.0:8 3.0:4 |
4.0:12 3.0:8 |
4.0:8 3.0:4 |
|
| USB4 | Compulsory (External, Using 4 Chipset PCie 4.0 Lanes) |
optional | |||
| SATA Ports (Maximum) | 8 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 4 |
| DDR5 Support | Quad Channel (128-bit bus) | ||||
| wifi | Wi-Fi 7 (External) | Wi-Fi 6E (External) | |||
| CPU Overclocking Support | Yes | ||||
| RAM Overclocking Support | Yes | ||||
| Silicon | ASMedia Promontory 21 | ||||
Conclusion
The Ryzen 9000 series comes with the benefits of Zen 5 architecture to counter not only Intel’s existing Raptor Lake Refresh chips, but also the yet-to-be-announced Arrow Lake processors. To summarize, the 16% IPC increase meets expectations in terms of performance, while the up to 40% improvement in TDP for lower-end models is quite positive news.
Arrow Lake will come with plenty of innovations, as well as Intel’s new 20A process technology, which will include the first backside power dissipation (PowerVia) and GAA—RibbonFET transistors. The chips are also said to come with the new Lion Cove P-Cire and Gracemont E-Core; This is again an important step.
Long story short, we can say that an extraordinarily competitive desktop PC market awaits us as we enter the second half of the year.

